Explanation of Power Factor
A Battery charger’s power factor rating can be explained as its abilityto effectively use incoming AC power. The more efficiently the battery charger uses incoming AC, the higher the power factor it will have and the less AC power it will consume. With less incoming AC power required by the battery charger there is more available AC power available for a battery systems on the vehicles.
The power factor correction (PFC) circuit is designed to draw a sinusoidal current from the AC input line that is exactly in phase with the input voltage. As a result, the battery charger exhibits a power factor that is very close to unity or one, which is ideal.
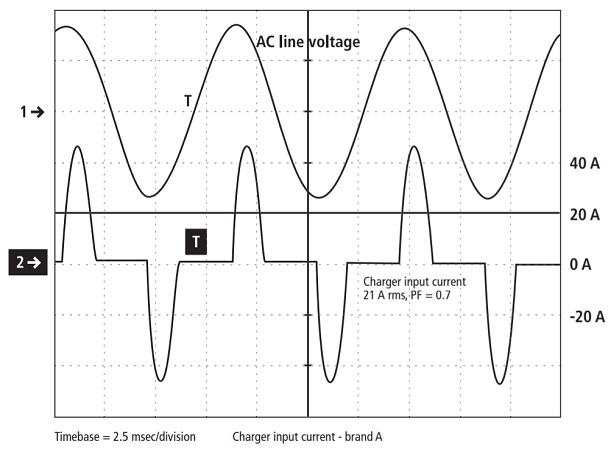
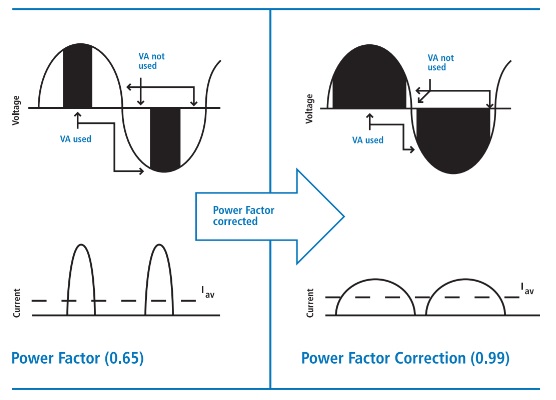
Steady-load power factor corrected converters are rated at greater than 0.95 power factor, compared to a rating of approximately 0.7 power factor for converters that are not power factor corrected. The improved power factor results in approximately 30% less AC input current required to deliver the same DC charging current.
Power factor correction methods
There are two common types of power factor correction for power supplies; the passive PFC and the active PFC.
Passive Power Factor Correction
This is used for small power supplies of about 100W or less. The correction method uses a low pass harmonic filter at the AC input with the capacitor and inductor forming a series resonance circuit. The components can be fairly small while providing an inexpensive and efficient power factor correction.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Active Power Factor Correction
The active PFC methods are preferred for power supplies of over 100W. This method provides a more efficient correction, is lighter and less bulky.
A basic active PFC circuit consists of a control circuit that measures the input voltage and current and then adjusts the switching time and duty cycle to ensure that the input voltage and current are in phase. This provides an automatic correction of the input AC voltage, resulting to a theoretical power factor of over 0.95. Unlike the passive PFC, the active PFC operates over a wide range of input voltages. However, it requires extra components, which makes it more complex and expensive.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Benefits to PFC Charging
The battery charger is high power for electric vehicles. A significant benefit of Steady-load power factor corrected (PFC) converters is that more of the incoming AC power to an battery system is available for charging.
PFC charging minimizes the amount of AC power needed to run your charger at full power. This maximizes available AC power usage, and increase the charging speed. It reduces the risk that AC loads running during battery charging will overload the system and trip the incoming AC circuit breaker.
Another benefit of PFC charging is the significant reduction in electrical noise, minimized through its phase-matching of input current draw to the input voltage, so it does not interfere with the operation of TVs, radios and satellite receivers.
All Steady-load converters feature power factor corrected charging for low electrical interference and maximum AC power available to the power-hungry Electric Vehicles.
PFC Charging Example
The following example highlights the advantages of a Steadyload power factor corrected battery charger. Both products listed below supply the same real power for charging, but the Steadyload converter requires less AC current to achieve the same result.
| Steadyload Charger | Competitor's Charger | |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Voltage | 66V | 65V |
| Charging Current | 35A | 30A |
| Charger Power | 2300W | 1920W |
| Efficiency | 95% | 85% |
| Power Factor | 0.99 | 0.90 |
| Input Current | 11A | 14A |